The Sportal365 CMS lets journalists/editors create and manage four major types of content – Articles, Videos, Galleries, and Images–to meet the diverse consumption habits of their audience. All content types follow a similar creation and optimization logic and can be displayed as a separate entity on your website.
While all types of content can appear on your website on their own, they can also be combined to deliver richer and more informative content; articles can contain videos, image galleries, and widgets, videos can include a body of text, images, and widgets, and so can galleries.
The optimization of each content type happens with a set of content properties available in the system, which will be explained in detail in the Content properties for specific content titles section.
Articles
The CMS allows journalists and editors to easily create and manage rich sports-focused articles. To better understand the general idea and possibilities when creating articles, consider the following:
Articles are more than just text.
The Sportal365 CMS is designed to deliver more than text-only articles. The system offers a set of editing tools and features that help journalists optimize and develop their content into rich sports-specific articles.
Article bodies are broken down into blocks, where creators can inserts text, but also different types of content, statistical and social media information as supporting materials–videos, image galleries, contextual widgets, statistical data, social media feeds, and more–, so their editorial content best meets the preferences of their audience.
See Content properties for specific titles and Widgets.
Articles need three components to be created.
To create a new article inside the system, three elements must be in place–a Title, a Category, and an Author. If those three fields are not occupied, you won’t be able to create, save, or publish a new article.
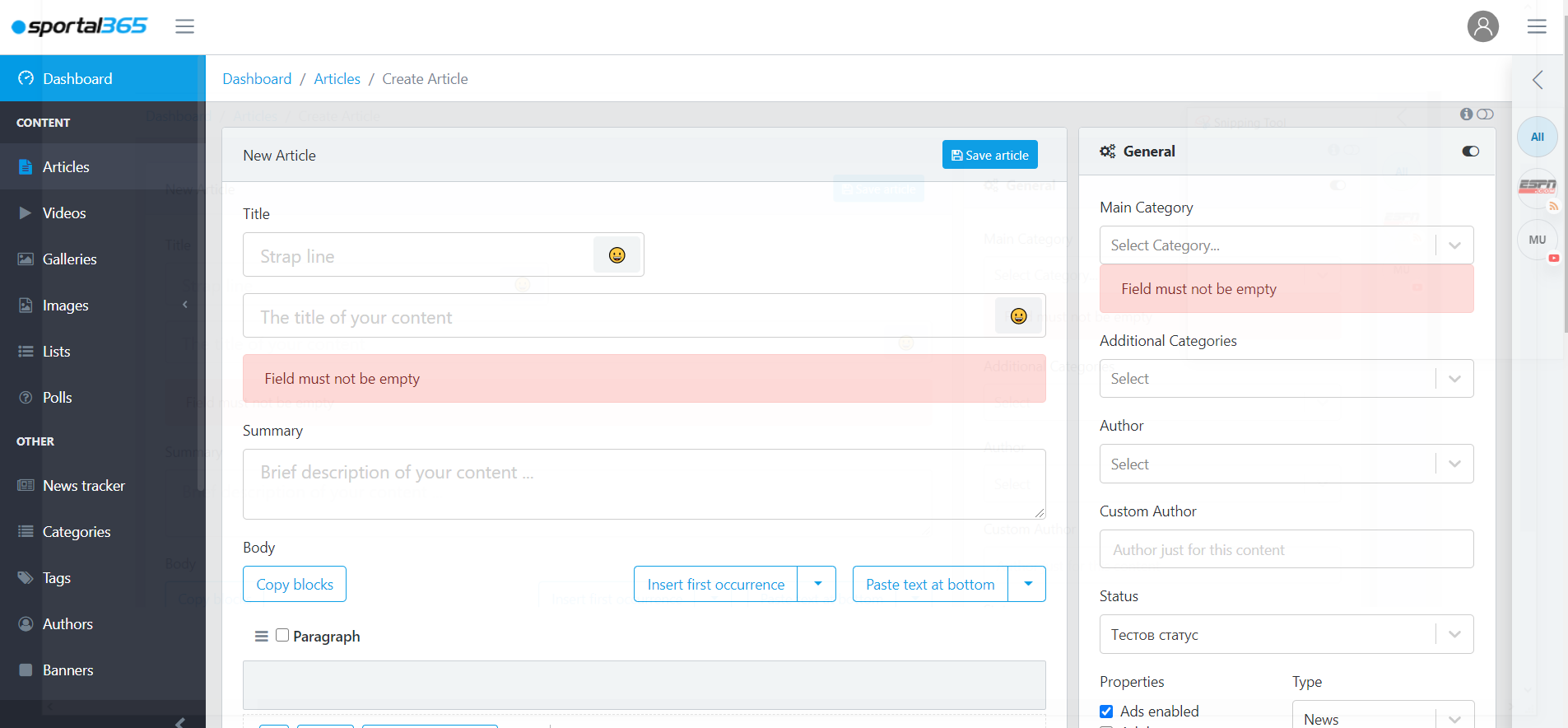
Articles are written and edited in blocks.
The body of articles is broken down into blocks, or what we call the Blocky. Each block has an editing panel, which allows journalists to polish and develop their content. Blocky lets creators highlight important passages in articles, insert contextual widgets and football statistics, as well as combine various types of content inside the body of their articles.
Writing in blocks optimizes the content-creation process easier, and makes possible the native display of content on mobile devices.
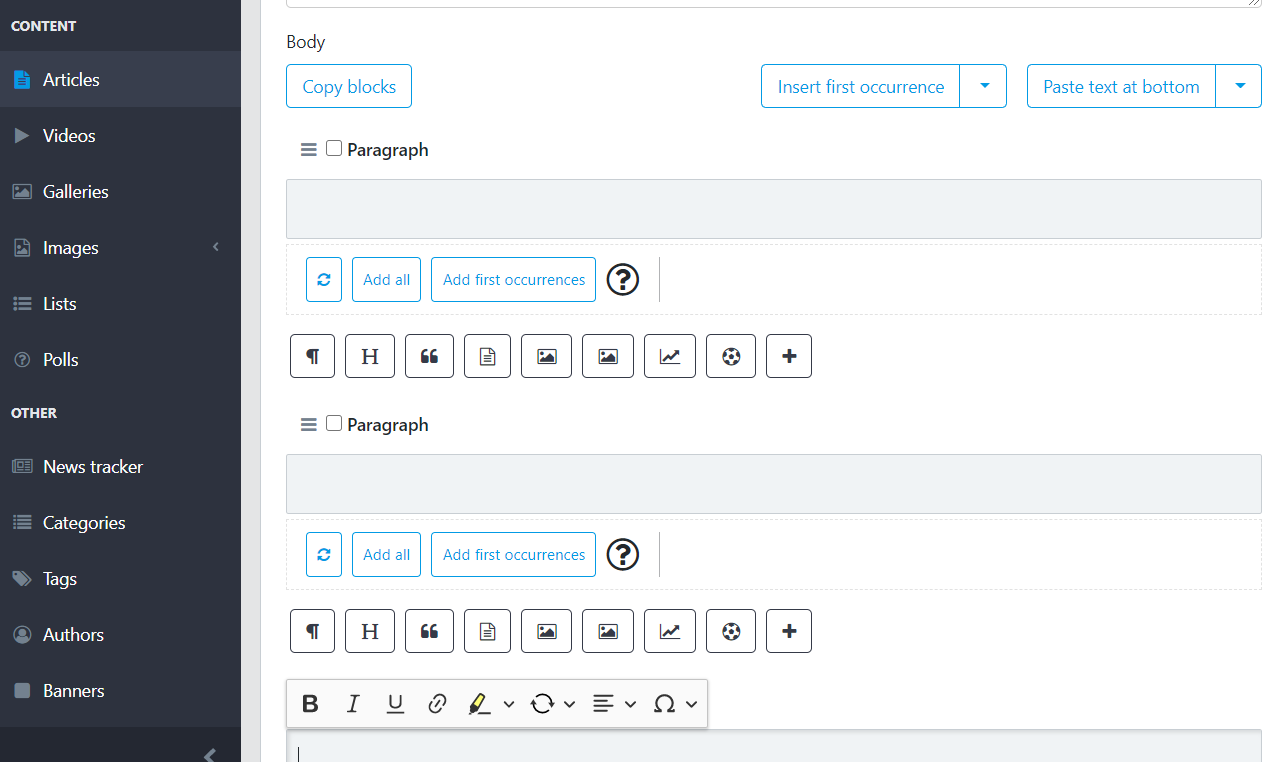
See Blocky.
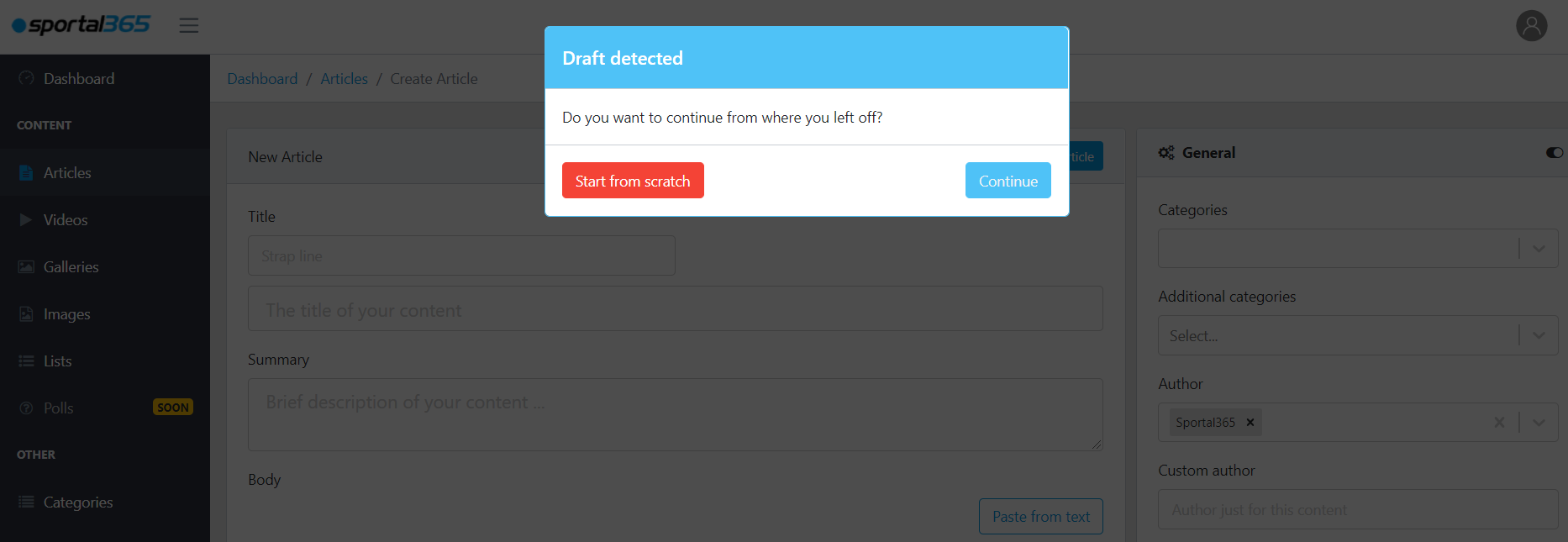
Articles can be saved as drafts.
To make work easier, the CMS saves drafts of your articles. If you start creating a new article, and for some reason, you exit your editing screen–the system saves a draft locally and you can later continue where you left off.
Articles can be previewed.
You can preview articles in two ways.
Your first option is to do it from your article library. You will notice the preview option next to each article in the library.
Alternatively, you can preview your article while you are working on it. Simply select the Preview button next to Save at the bottom of the page.
Articles can be optimized.
Each article created inside the CMS can be optimized with a set of content properties under the tabs–General, Media, Tags, Related content, URLs, SEO. These tools help enrich your content, distribute articles better online and make it easier for readers to navigate your website and find the articles they want.
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1575647110346&cacheVersion=1&api=v2)
Please see Content properties for specific content titles where content optimization tools are explained in detail.
Articles can be used as supporting content in other content types.
Once you create an article, it goes to your article library and you can then reuse it and insert it as secondary/supporting content inside the body of another content type (videos or galleries).
Videos
Videos are a popular content format with a main body, components, and general creation logic almost identical to that of articles and galleries.
What is specific for Videos?
Videos are uploaded and shared in two ways.
Embedded video – One way to upload а video from the CMS to your website is if you embed it. You can embed all types of videos simply by copy-pasting the embed code in the Media tab of your video content properties sidebar.
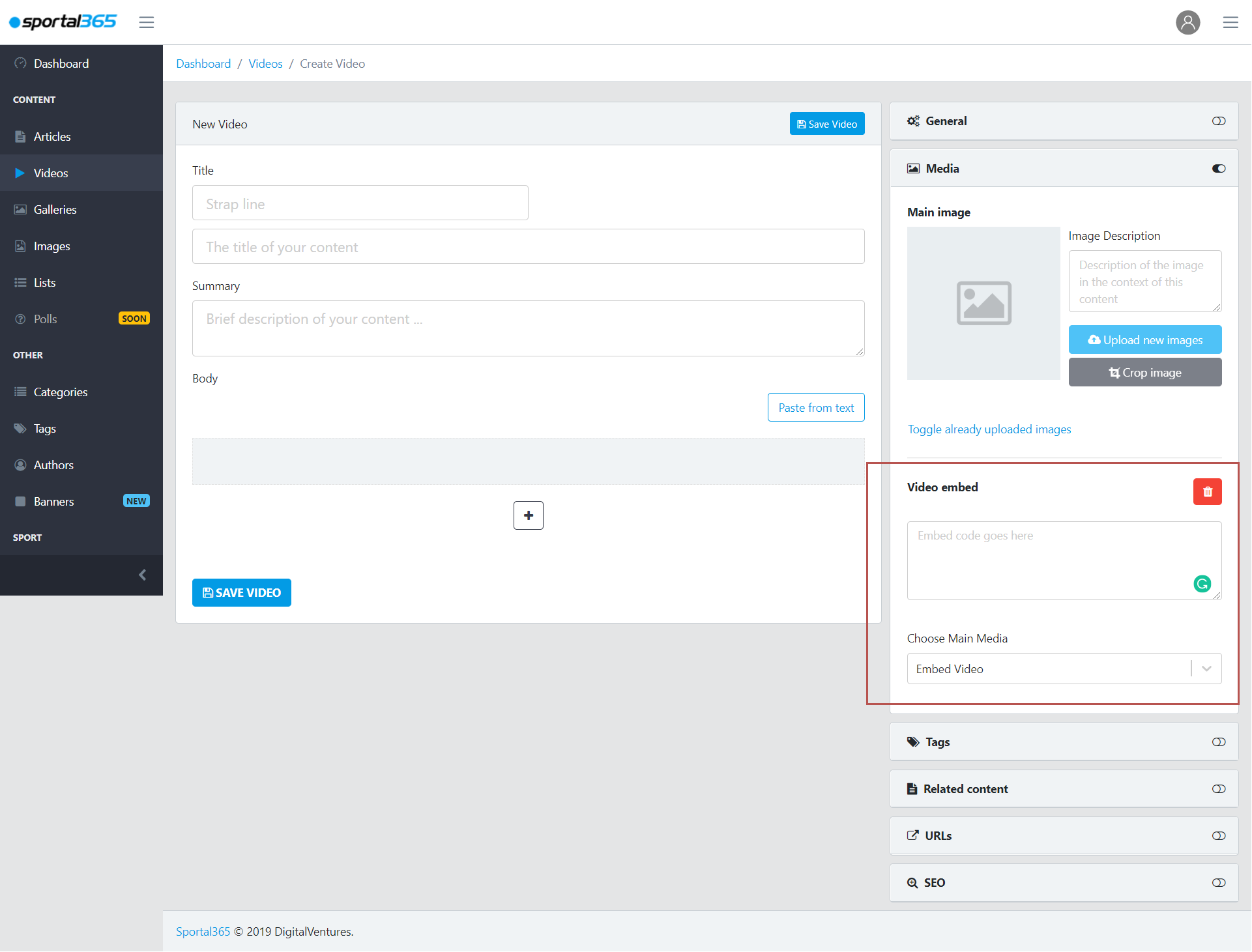
Live URL – Another way to share a video from the CMS to your website is by using the Live URL functionality of the system. This is often used by journalists when they cover events taking place in real-time. The live URL is under the URLs tab of your video content properties.
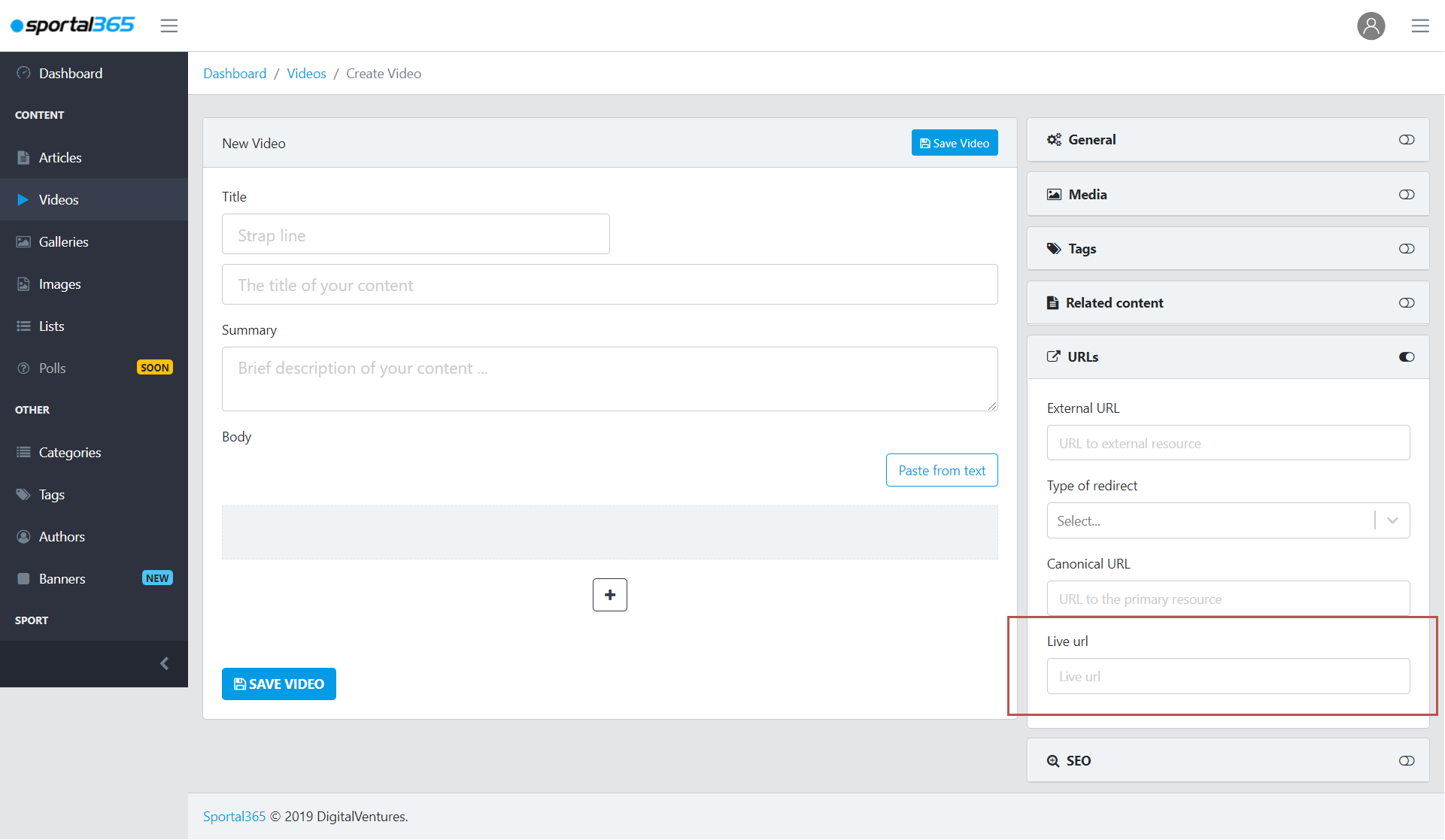
To share a Live URL, you need a link to a RTP stream, such as rtp://somewhere.com/sadasd. RTP is a protocol used for transporting audio and video in real-time over IP networks. The transport used can be unicast, multicast or broadcast, depending upon transport address and port.
See Content properties for specific content types.
Similarities with other content types.
Videos can combine other content types, statistics and social feeds inside their bodies.
Similarly to articles, videos need three components to be created.
The main body of videos is written and edited in blocks.
Videos can be optimized.
Videos can be used as supporting content in other content types.
Galleries
Galleries have a main body, components and general creation logic almost identical to that of articles and videos.
What is specific for Galleries?
You can upload new images or use already uploaded images in a new gallery.
When you create a new gallery or edit an existing one, you will notice two tabs inside Galleries–а Content tab and an Items tab.
The Content tab is where you edit and optimize galleries in the same way you do articles or videos.
On the other hand, the Items tab is where you add images and image comments to a newly created gallery. You can add already existing images or upload new ones to your new gallery. Images uploaded to your gallery are saved into your images library and can be reused in other galleries you want to create.
Note that you can upload multiple images to your gallery at once.
You can comment on an image in the context of a specific gallery.
Once you select/upload the images for the new gallery that you want to create, you can comment under each image.
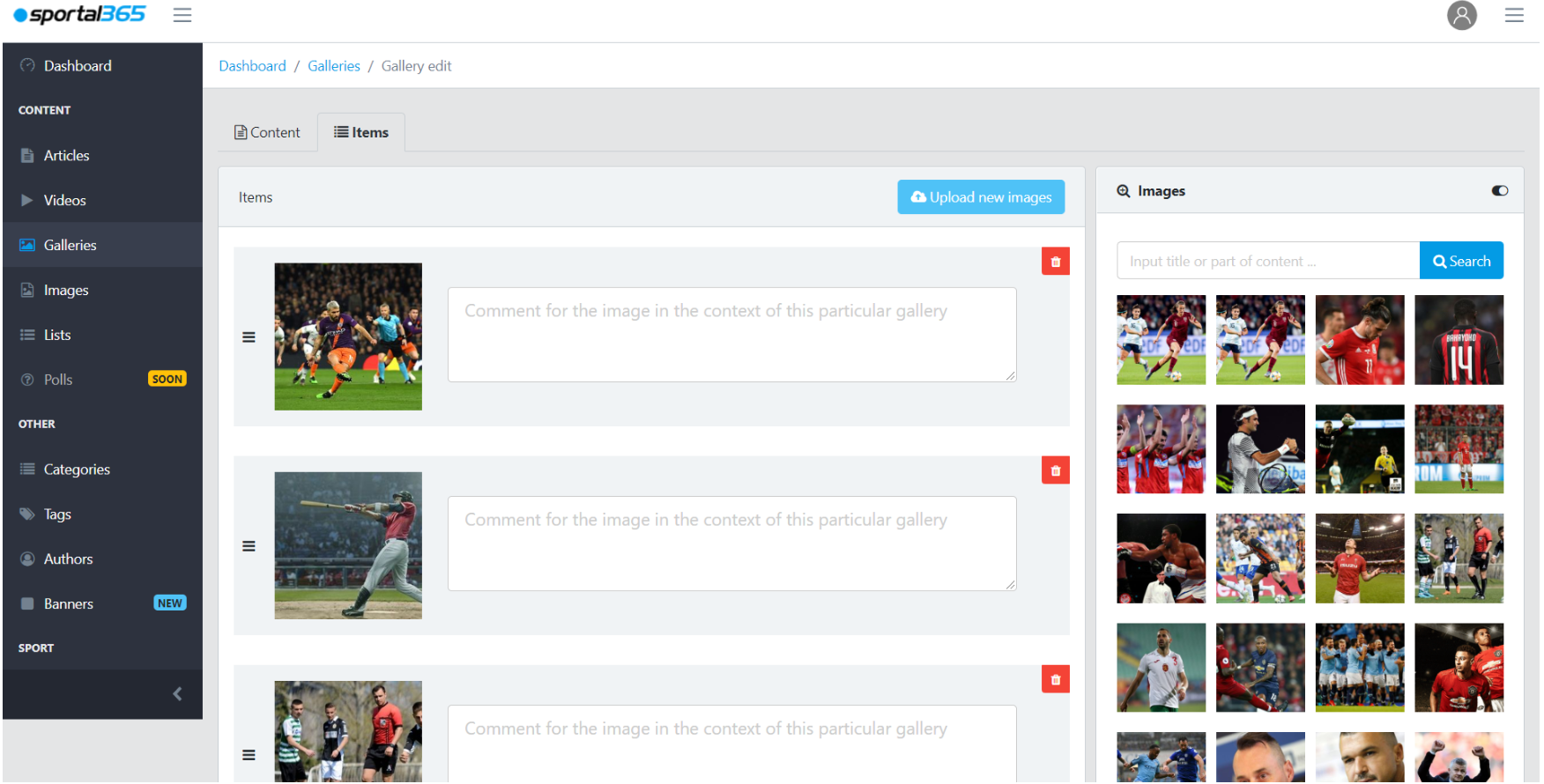
Comments you leave under each image in your newly created gallery will appear only in that specific gallery. If you decide to use the uploaded images in a new gallery, the commentaries won’t appear.
Also, when you use a gallery as a supporting/secondary content inside the body of another content type, the images in the gallery will appear with the comments written when it was created.
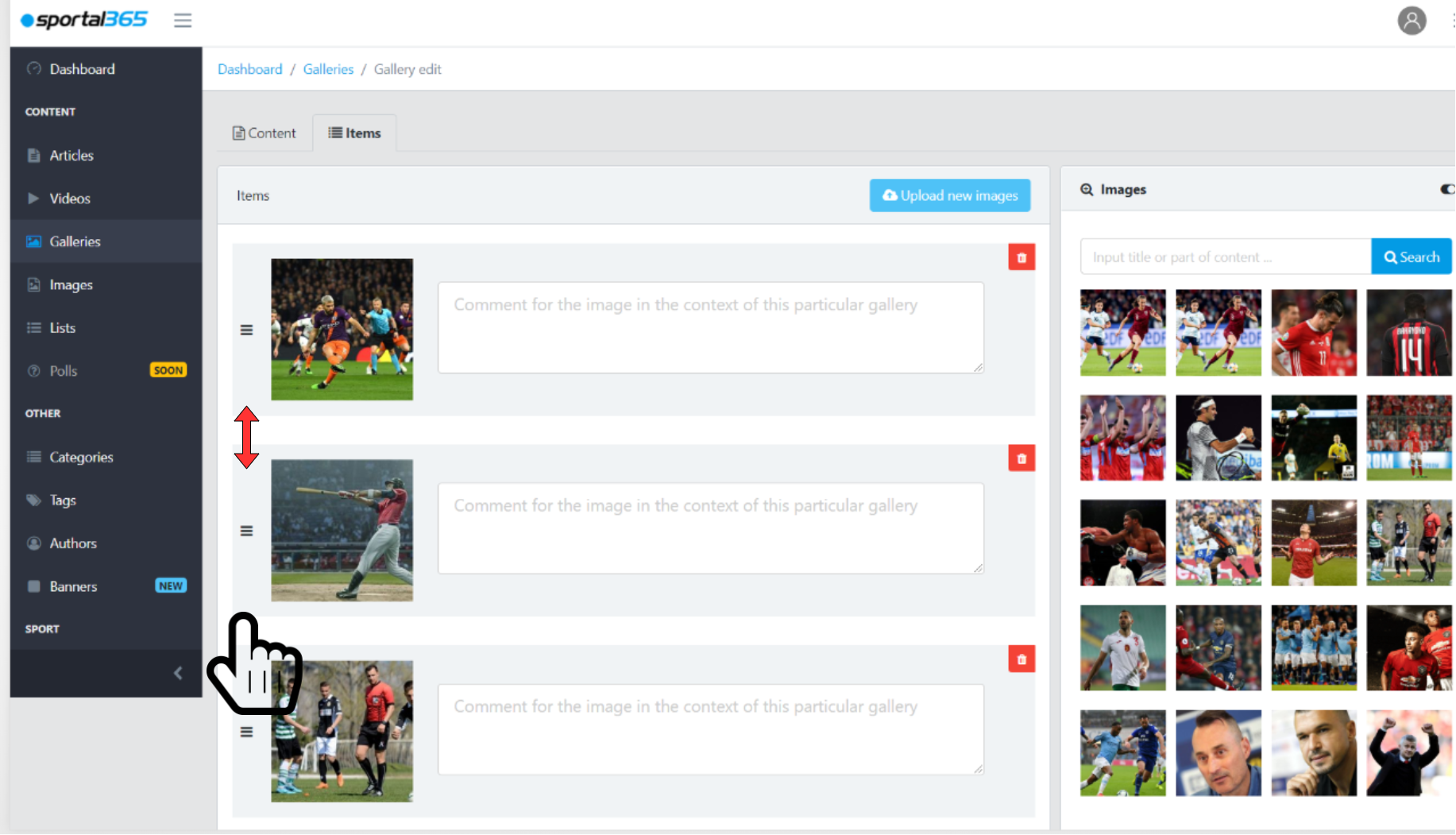
You can drag/drop to rearrange the position of images in your gallery.
You can easily reorder images in a gallery by dragging and dropping them up and down.
Similarities with other content types.
Galleries can combine other content types, statistics and social feeds inside their bodies.
Similarly to articles and videos, galleries need three things to be created.
The main body of galleries is written and edited in blocks.
Galleries can be optimized.
Galleries can be used as supporting content in other content types.
Galleries can appear as a separate entity on your website.
Images
Images is the content type that differs in its creation and editing logic from the rest.
What is specific for Images?
Images can be uploaded one at a time or many at once.
The Sportal365 CMS supports single image upload and multiple.
Images don’t have a body and cannot be edited in blocks.
Unlike all other content types, images don’t have a main body (Blocky). Images are uploaded to the system’s image library and can only be updated with a description, source and tagged with a football connection.
Images have descriptions instead of content properties for optimization.
The optimization of images inside the system differs from that of the other three content types. You will notice that inside the CMS, images don’t have the content property tabs (General, Media, Tags, Related content, URLs, SEO) used to enhance videos, galleries, and articles.
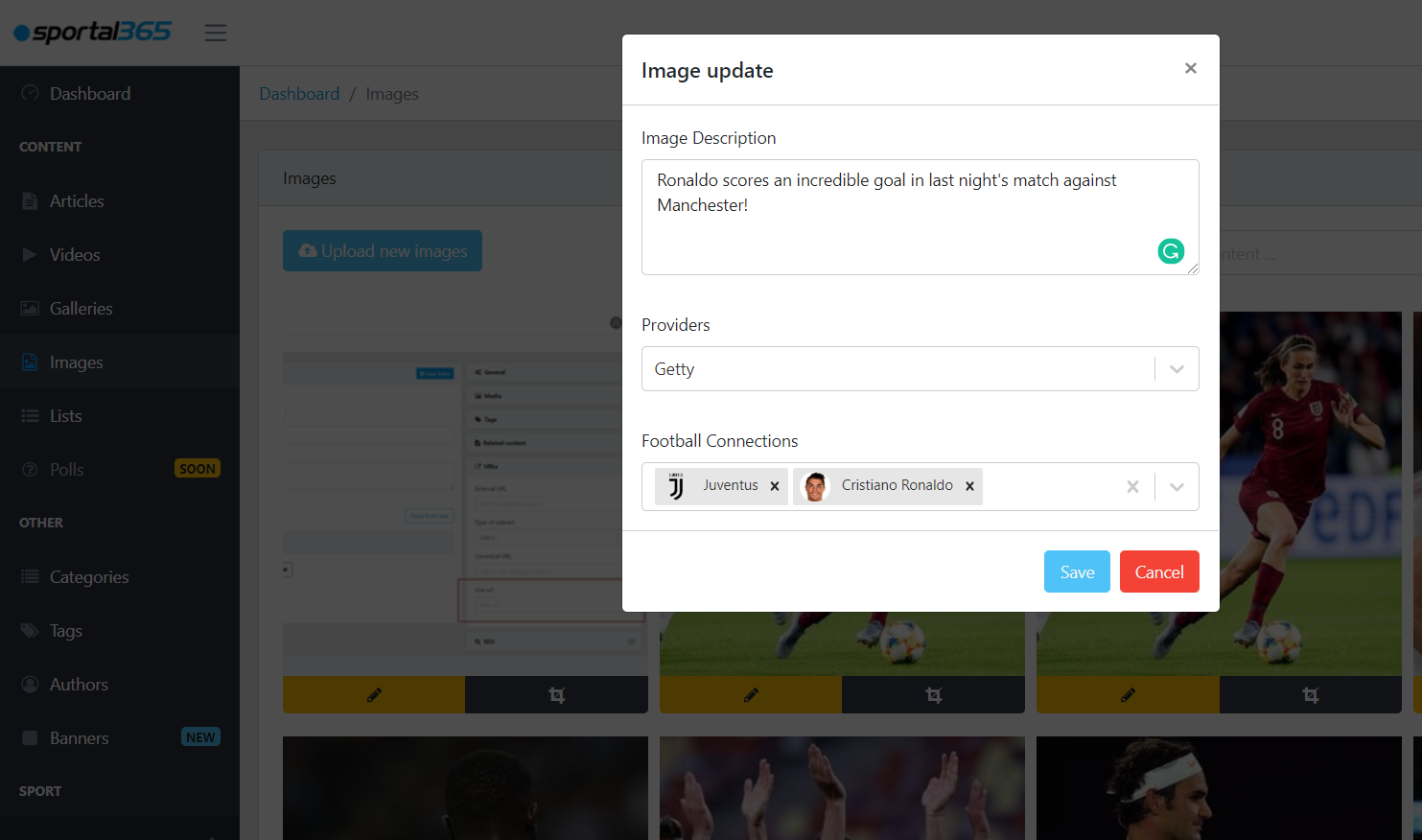
Images have descriptions, providers and football connections.
Descriptions. Image descriptions create a better context for viewers and improve search and SEO results. The description you write after you upload an image can either remain the same or it can be later overwritten with a new description when an image is used as main media in articles, thumbnail in videos as supporting content inside the body of the other three content types. As headless CMS, we leave it up to you to decide what description to display on your website.
Providers. Providers is the field where you specify the source of the image. For example, it could be Getty Images, Shutterstock or the name of your media if an image is taken by your team.
Football connections. Images are tagged with football connections–teams, players, games–relevant to what is actually on the picture for SEO purposes, better search, and segmentation of your website.
See Content properties for various content types for more information.
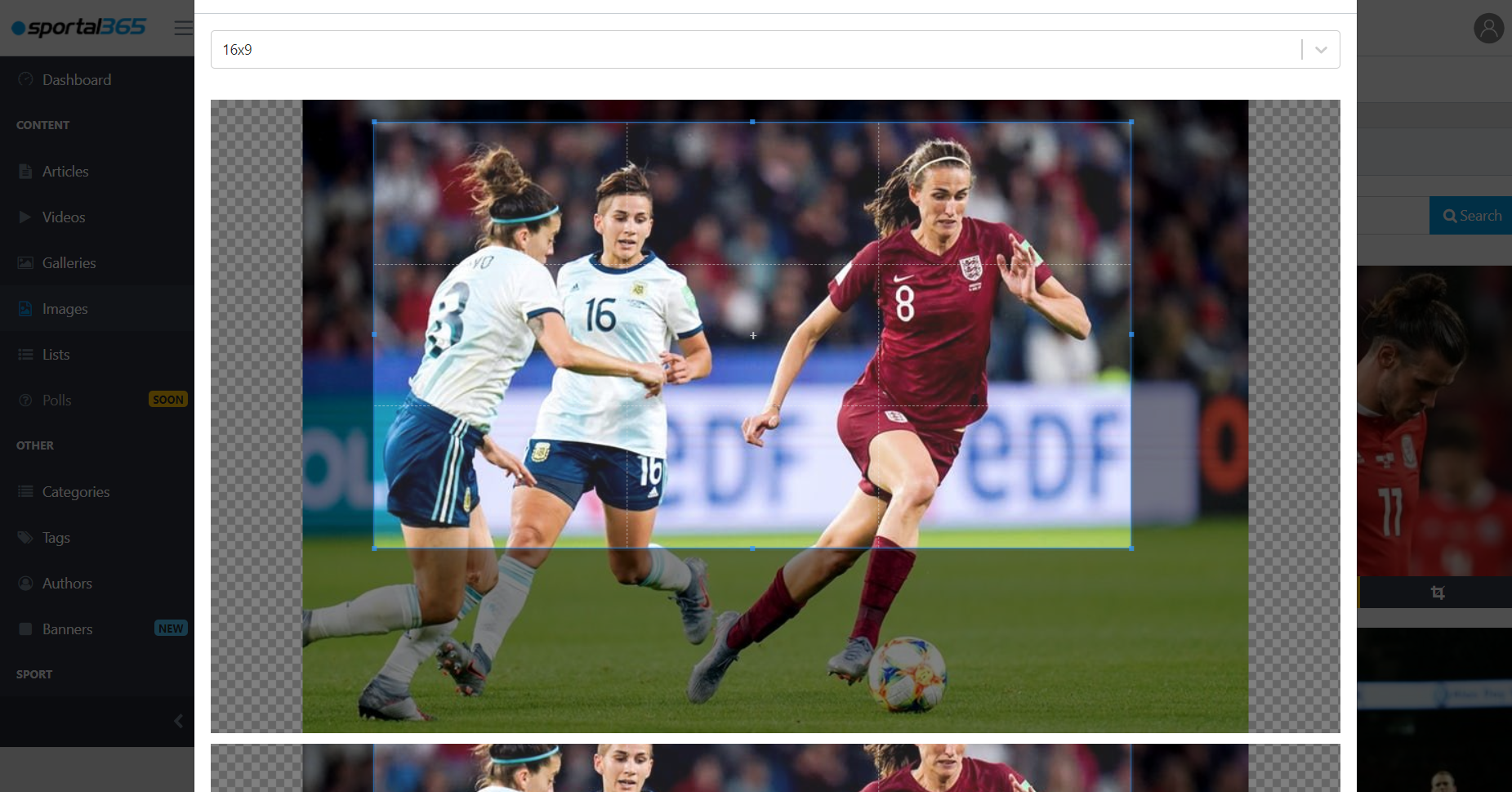
You can crop or change the ration of images.
Once you upload an image to your image library, you can crop it or change the image ratio. You can choose from several aspect ratios: 16x9 / 9x16 / 4x3 / 4x3 / 2x3 / 3x2 / 1x1.
Images can also appear as separate entities on your website.
For images to appear as a separate entity on your website depends entirely on your front-end set up. An image can appear as a separate entity on your website under, for example, a “Picture of the day” section.
Similarities with other content types:
Images can be used as supporting content in other content types.
Similarly to the other content types, images can be reused in videos, articles, and galleries. Once you upload an image to your image library, you can then insert it as secondary/supporting content inside the body of another content type (video, article or gallery).
However, you can select an image to be the main media of an article, a thumbnail for a video, or one of the pictures when you upload a new gallery.



.png?version=1&modificationDate=1575647110346&cacheVersion=1&api=v2)





